What is an Asset?
The first thing we should know before discussing Asset lifecycle management is; What are assets? Assets, (in the world of IT), can be defined as any piece of equipment that a person or an organisation owns. So, it can range from a mobile phone to an entire data centre of IT hardware. This blog will discuss tech assets such as computers, servers, laptops, and storage media like hard disks, SSD, etc.
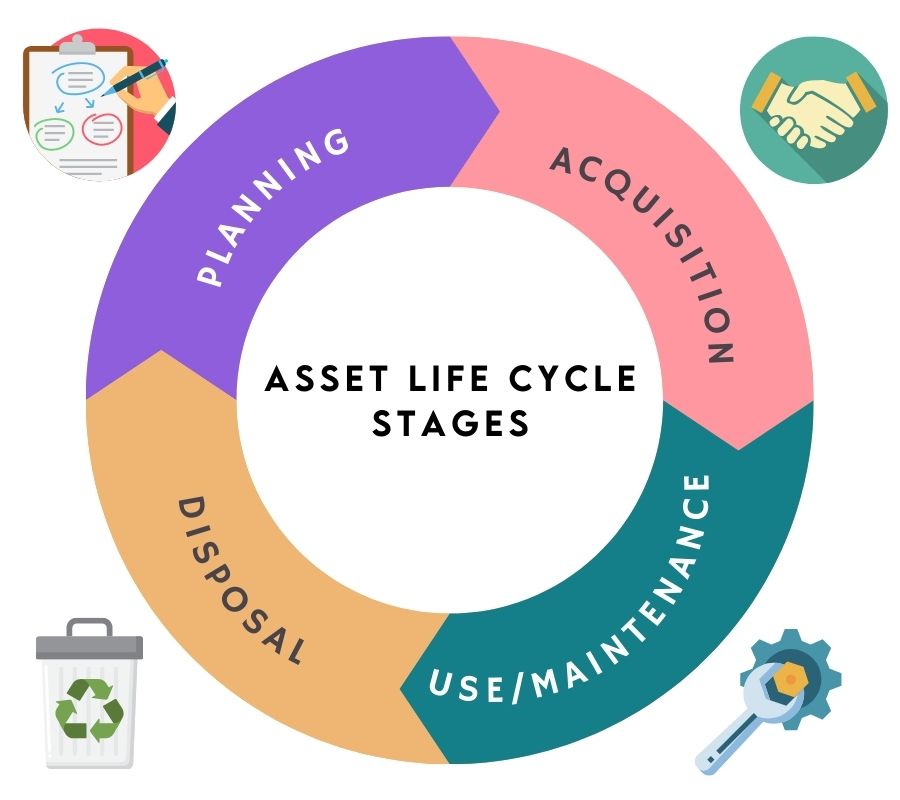
Asset Lifecycle
An asset’s life cycle is the duration from when you think of buying the asset to when it is no longer usable and has to be disposed of. When the asset is ready to be retired, it is considered at the end of the Asset life cycle. The asset lifecycle consists of other stages, such as the acquisition and the usage of the asset. One of the most crucial stages in Asset lifecycle management is maintenance.
Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset lifecycle management is a timed process for assets whereby you figuratively move assets through a schedule from the start (installation) to finish (decommission & asset disposal). Since assets have a limited lifecycle, it is crucial to manage effectively and sweat them before disposal. Thus it is crucial to have a strategy in place. You could consider extending the lifespan of the assets but this would require consideration of maintenance costs, spare parts, and battling the ever-growing requirements to increase performance.
Why is asset lifecycle management important?
Every organisation has certain assets on its premises, or in data centres. Generally speaking, large organisations have more assets, and small organisations have fewer assets. Still, regardless of the organisation’s size, assets play an essential role in the organisation’s day-to-day work. Without assets, the manpower in organisations becomes useless, and vice versa.
Every asset plays its part in the organisation. Assets keep the IT side of business performing as intended, yet require maintenance over time. It is savvy business practice to sweat your IT assets as long as possible… up until the point that the assets are ready to be disposed of – along the way they may need maintenance. Tracking, optimising, and managing your assets have its benefits. Some of the benefits of asset life cycle management are as follows:
Extend the lifespan of the Assets
Managing your assets will help in extending their lifespan. Properly tracking your asset’s lifecycle will give better insights into the working condition and if/when they need repairs and maintenance. These insights will help you find the optimal time for repairing so that it is continuously operating in its peak condition.
Properly analysing patterns enables your asset to work at their absolute best with preventive maintenance when necessary. Asset Maintenance will surely help to extend the lifespan of the assets.
Reduce the downtime of the assets
If you are following an asset lifecycle management plan, it will help to reduce downtime. You won’t need to perform reactive maintenance, ultimately decreasing the assets’ downtime. Pre-planned scheduled maintenance will help avoid addressing urgent business critical tasks so you can schedule accordingly.
Also, planning in scheduled maintenance operations outside business hours will ensure time is well-spent on sudden updates.
Increases efficiency
One significant benefit of asset lifecycle management is that your assets are always in peak-performing condition. Having your assets in peak performing condition will guarantee increased efficiency in the workplace. Peak-condition assets have a longer lifespan and less downtime, improving overall efficiency.
Saves money
It is no brainer that efficient assets will help you save money in the long run. Maintaining and repairing assets will be cheaper and better than purchasing new assets. A properly executed asset lifecycle management plan will ensure that your assets have a longer life cycle. A longer life cycle means you won’t need to purchase new assets for an extended time.
Also, planned maintenance operations cost less money than sudden reactive maintenance. Scheduling your maintenance will help you to save money on unwanted reactive maintenance.
Better Future decisions
Using a systematic Asset lifecycle management plan, you can retrieve valuable information regarding your assets and their workings that could be beneficial for making future decisions. Making decisions for the budget will be easier when you know what assets need to be repaired and what needs to be replaced.
Stages of Asset Life Cycle Management
Asset lifecycle management is a strategic approach to get maximum usage out of assets and, in the meantime, reduce costs and increase the life cycle of the assets. The overall process has to be carried out in different stages.
Planning
The first stage in the Asset management lifecycle is the realisation that you need a specific asset in your organisation. You would need new assets because your organisation lacks assets to carry out your tasks. Then you figure out what assets you exactly need and start the planning process.
The planning phase can be challenging. Assets that cost you a few dollars are not a big deal, but some assets require considerable budgets, which need more consideration. It would be best to compare different products and models of assets that can deliver your organisation’s requirements and fall within your company’s budget. After exploring various options, you must fix one and proceed with the process.
Acquire/Procuring
You purchase the assets once you’ve locked in your choices. Acquiring isn’t limited to just buying the product. Some assets need installation and delivery into your facility. Some assets may require expert assistance to install and operate, and some assets require software to run on the hardware. Only after the asset is delivered, installed, and fully functional can you move on to the next stage.
Also, installation costs during the delivery of the asset must be added to the asset’s price. Now that the asset is installed and operable, you can use it for its intended use.
Use/Maintenance
After acquiring the asset, you are now ready to benefit from its service. The asset will now fulfil its intended purpose for which the organisation purchased it. The designated person will use the asset to carry out the task. After some use, the assets would require timely maintenance and repairs. You will need to create a maintenance strategy for the assets. Strategic routine maintenance is the best for an asset as it can save money and keep it in peak-performing condition.
Keeping in mind an optimal time to schedule in maintenance will help extend the asset’s life span and deliver maximum efficiency.
You can create maintenance management plans as time-based, condition-based or metre based according to the asset. Create a clear maintenance checklist to ensure every aspect of the asset is adequately monitored and maintained.
Use and maintenance are the asset management lifecycle’s longest and most important phases. Maintenance doesn’t just mean repairs; it could also be upgrades and modifications to the assets to keep them in peak working condition. Maintaining an asset is very important because it works towards and ensures the following things:
- Prolonging life span of assets
- Reducing surprise repair costs
- Lesser Asset Downtime
- Higher Efficiency of Assets
- Higher profits due to longer lifespan and better efficiency
Dispose
Nothing is permanent in this world; just like everything, these assets must be disposed of after a particular time. After years of usage, and multiple repairs/maintenance procedures, the assets reach a point where replacing them with new ones becomes a better option than repairing them. You can perform a cost-benefit analysis to determine whether repairing the machine again would be better than buying a new one. The efficiency becomes very low and repairs cost pile up. At that point, asset disposition is the only way to go.
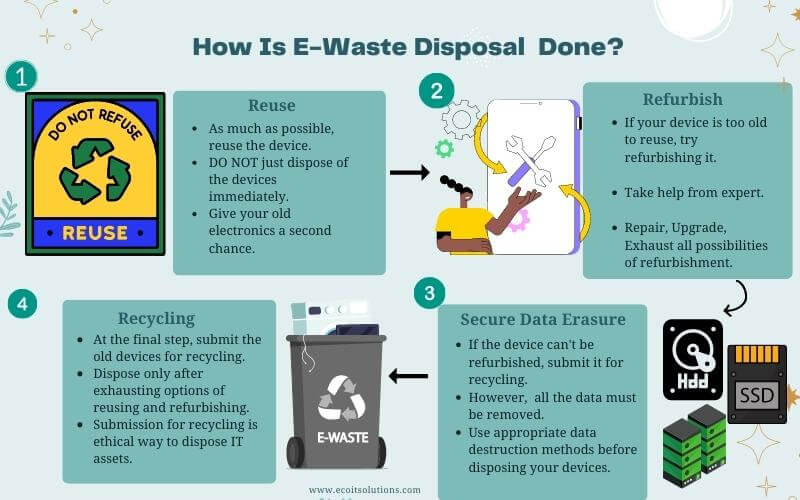
Disposing of the asset doesn’t mean you need to throw them away as E-waste. There are different options you can look into while removing the assets.
- Is there a potential buyer for the used asset?
- Can the asset be refurbished and resold?
- Can the assets be donated to someone?
You can look into these options and dispose of the assets, whichever suits you. After the asset has been disposed of, the cycle is complete and restarts again. You now find a replacement for the asset, and you have to plan again. The disposed asset should never be thrown away in a landfill due to the negative environmental impact as well as the protection of your data. You can always call an E-waste recycling company to take the e-waste from your business premises, and they will take care of everything.
So, this completes the entire process of asset lifecycle management. Contact Eco IT Solutions if you want guidance regarding the Asset lifecycle management for your organisation.